Introduction
Non woven fabric manufacturing is a complex and intricate process that involves a number of steps. The process begins with the selection of raw materials, which are then passed through a series of machines that perform various operations to convert them into finished products.
The non woven fabric manufacturing process is carried out in two main stages: the spinning stage and the finishing stage. In the spinning stage, the raw materials are converted into yarn, which is then used to weave the fabric. In the finishing stage, the fabric is given its final shape and properties.learn more(wikipedia)
The non woven fabric manufacturing process is a heavily automated process that requires a high level of coordination between the various machines and the workers. In this article, we will give you a complete guide to the non woven fabric manufacturing process.
Raw Materials Selection
The primary raw materials used in non woven fabric manufacturing include fibers such as polyester, polypropylene, nylon, and rayon. These fibers are selected based on their properties such as strength, color, and texture.
Preparation
The fibers are first cleaned and made free from any impurities. The fiber is then processed into smaller filaments through mechanical methods such as carding or combing. Alternatively, synthetic fibers are melted and extruded as fine threads.
Web Formation
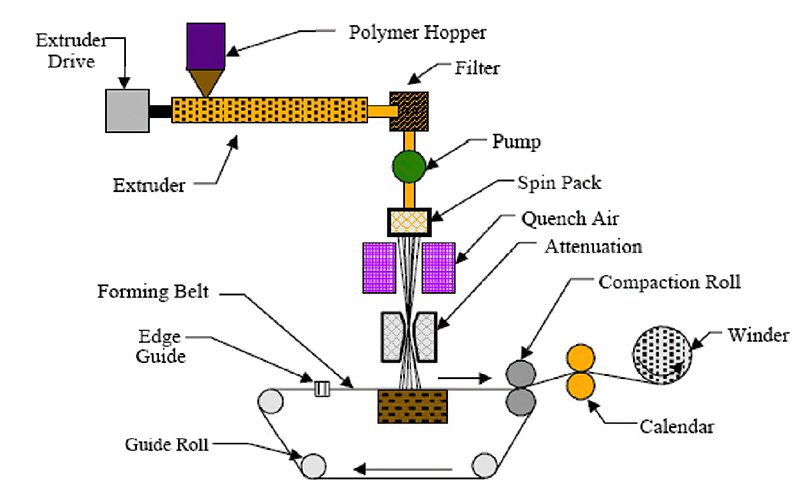
The next step involves the formation of a web from the prepared fibers. This can be done through various techniques such as air laying, carding, or spunbonding.
- Air Laying – The fibers are blown through a nozzle and deposited onto a conveyor. This technique allows the fibers to be deposited uniformly and randomly.
- Carding – The fibers are placed through a series of rollers which separate and align the fibers into a web.
- Spunbond – In this process, molten polymer material is extruded to form continuous filaments. The filaments are then laid on a conveyor belt and bonded together with heat and pressure.
Bonding
Once the web is formed, it must be bonded together. This is done through various techniques such as thermal, mechanical or chemical bonding.
- Thermal Bonding – In this process, heat is used to melt the fibers and bond them together.
- Mechanical Bonding – In this process, the fibers are mechanically entangled with each other through needles or water jets. This technique results in a stronger and more durable fabric.
- Chemical Bonding – In this process, chemicals are used to bond the fibers together at a molecular level.
Finishing
After bonding, the fabric is given its final properties such as strength, water resistance, or fire resistance. The fabric may also be treated with dyes or coatings to improve its appearance or functionality.
Cutting and Packaging
The final step involves cutting the fabric according to the desired size and packaging it for shipment.
In conclusion, the non-woven fabric manufacturing process is a complex and automated process that requires specialized equipment, skilled labor, and a thorough understanding of the properties of different materials. Non-woven fabrics have wide applications in various industries due to their unique properties such as lightweight, durability, and water resistance. The popularity of non-woven fabrics is expected to continue to grow as more industries recognize their benefits and eco-friendliness.