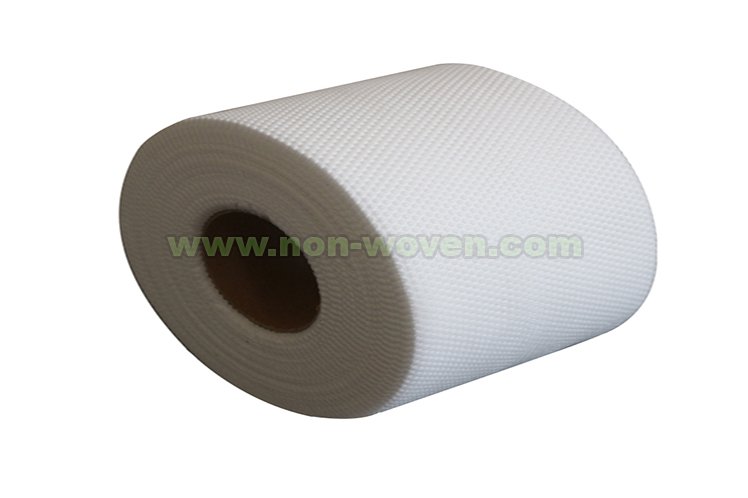
The Ultimate Showdown: Spunlace vs Airlaid – Which Nonwoven Fabric Reigns Supreme?
Introduction:
Nonwoven fabrics are versatile materials that are used in a wide range of industries, including healthcare, hygiene, cleaning, automotive, construction, and agriculture. They are made from fibers or filaments that are bonded together through mechanical, chemical, thermal, or other means, without weaving or knitting. Nonwoven fabrics are known for their softness, strength, absorbency, barrier properties, and cost-effectiveness.
Two popular types of nonwoven fabrics are spunlace and airlaid. While they share some similarities, they have distinct differences that make them suitable for different applications. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between spunlace and airlaid, and help you decide which one is the best fit for your needs.
Outline:
I. Introduction
II. Spunlace Nonwoven Fabric
A. Definition and Characteristics
B. Manufacturing Process
C. Applications
D. Advantages and Disadvantages
III. Airlaid Nonwoven Fabric
A. Definition and Characteristics
B. Manufacturing Process
C. Applications
D. Advantages and Disadvantages
IV. Comparison between Spunlace vs Airlaid
A. Physical Properties
B. Performance Properties
C. Cost Comparison
V. Case Studies
VI. Future Trends
VII. Conclusion
Table:Spunlace vs Airlaid
| Property | Spunlace Nonwoven | Airlaid Nonwoven |
|---|---|---|
| Basis Weight (gsm) | 30-200 | 40-800 |
| Tensile Strength (N) | 30-100 | 20-70 |
| Absorbency (ml/g) | 6-10 | 8-20 |
| Softness | High | Medium |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
II. Spunlace Nonwoven Fabric
A. Definition and Characteristics
Spunlace nonwoven fabric, also known as hydroentangled or spunlaced fabric, is made by entangling or intertwining fibers through high-pressure water jets. The fibers can be natural, synthetic, or a blend of both, and can be of different lengths and thicknesses. The resulting fabric is soft, smooth, and flexible, with a uniform structure and good strength.
B. Manufacturing Process
The process of making spunlace nonwoven fabric involves several steps, including:
- Fiber preparation: The fibers are first opened, blended, and carded to form a loose web.
- Web formation: The web is fed into a water jet entanglement machine, which sprays high-pressure water jets from multiple nozzles onto the web.
- Entanglement: The water jets interlock and compress the fibers, creating a strong bond between them.
- Drying and finishing: The fabric is dried, calendered, and sometimes treated with chemicals or additives to improve its properties.
C. Applications
Spunlace nonwoven fabric is used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Wipes: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is commonly used for wet wipes, dry wipes, baby wipes, makeup removers, and other personal care and cleaning products. It provides a soft, gentle, and effective cleaning surface, and can be impregnated with various formulations for different purposes.
- Medical: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is used for surgical gowns, drapes, face masks, wound dressings, and other medical products. It provides a barrier against fluids, bacteria, and other contaminants, and is comfortable and breathable for the wearer.
- Home textiles: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is used for bed sheets, pillowcases, mattress covers, and other bedding and upholstery products. It is hypoallergenic, durable, and easy to care for.
- Industrial: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is used for filtration, insulation, packaging, and other industrial products. It can withstand high temperatures, chemicals, and abrasion, and can be customized for specific needs.
D. Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of spunlace nonwoven fabric are:
- Softness: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is known for its soft and smooth texture, which makes it comfortable and gentle for the skin.
- Strength: Spunlace nonwoven fabric has good tensile and tear strength, which makes it durable and resistant to deformation.
- Absorbency: Spunlace nonwoven fabric has moderate absorbency, which makes it suitable for cleaning and wiping applications.
- Customizability: Spunlace nonwoven fabric can be customized for different fibers, basis weights, textures, colors, and finishes, to meet the specific needs of customers.
The disadvantages of spunlace nonwoven fabric are:
- Cost: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is generally more expensive than some other nonwoven fabrics, due to its complex and energy-intensive manufacturing process.
- Thickness: Spunlace nonwoven fabric may not be as thick or bulky as some other nonwoven fabrics, which may limit its use in some applications.
III. Airlaid Nonwoven Fabric
A. Definition and Characteristics
Airlaid nonwoven fabric, also known as drylaid or pulp-based fabric, is made by using air to disperse and bond fibers onto a porous surface. The fibers are usually wood pulp, but can also be other natural or synthetic fibers. The resulting fabric is absorbent, fluffy, and bulky, with a random structure and good insulation.
B. Manufacturing Process
The process of making airlaid nonwoven fabric involves several steps, including:
- Fiber preparation: The fibers are first beaten, refined, and screened to form a pulp.
- Web formation: The pulp is fed into an airlaid machine, which uses air streams to deposit the fibers onto a moving conveyor or drum.
- Bonding: The fibers are bonded together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical means, such as needle punching, heat treatment, or adhesive application.
- Finishing: The fabric is cut, folded, and sometimes treated with additives or coatings to improve its properties.
C. Applications
Airlaid nonwoven fabric is used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Absorbent products: Airlaid nonwoven fabric is commonly used for feminine hygiene products, adult incontinence products, baby diapers, and other absorbent products. It provides a high level of absorbency, fluid distribution, and odor control, and can be customized for different shapes and sizes.
- Food packaging: Airlaid nonwoven fabric is used for meat pads, cheese wraps, and other food packaging products. It provides a cushioning and absorbent layer that helps to preserve the freshness and quality of the food.
- Home and personal care: Airlaid nonwoven fabric is used for napkins, towels, tablecloths, and other home and personal care products. It provides a soft and fluffy texture, and can be embossed or printed for decorative purposes.
- Industrial: Airlaid nonwoven fabric is used for insulation, filtration, and other industrial applications. It can withstand high temperatures, chemicals, and pressure, and can be made with different fibers and finishes.
D. Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of airlaid nonwoven fabric are:
- Absorbency: Airlaid nonwoven fabric is known for its high absorbency and fluid distribution, which makes it suitable for a wide range of absorbent products.
- Bulkiness: Airlaid nonwoven fabric has a fluffy and bulky texture, which makes it suitable for cushioning and insulation applications.
- Customizability: Airlaid nonwoven fabric can be customized for different fibers, basis weights, densities, and finishes, to meet the specific needs of customers.
- Sustainability: Airlaid nonwoven fabric can be made from renewable and biodegradable fibers, such as wood pulp, which reduces the environmental impact of the product.learn more(wikipedia)
The disadvantages of airlaid nonwoven fabric are:
- Softness: Airlaid nonwoven fabric may not be as soft or smooth as some other nonwoven fabrics, due to its random and uneven structure.
- Compression: Airlaid nonwoven fabric may compress or flatten over time, which may affect its performance and appearance.
IV. Comparison between Spunlace vs Airlaid
A. Physical Properties
Spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric have different physical properties that affect their suitability for different applications. Some of the key differences are:
- Basis weight: Spunlace nonwoven fabric has a basis weight range of 30-200 gsm, while airlaid nonwoven fabric has a basis weight range of 40-800 gsm. This means that airlaid nonwoven fabric is generally thicker and more bulky than spunlace nonwoven fabric.
- Tensile strength: Spunlace nonwoven fabric has a tensile strength range of 30-100 N, while airlaid nonwoven fabric has a tensile strength range of 20-70 N. This means that spunlace nonwoven fabric is generally stronger and more resistant to tearing than airlaid nonwoven fabric.
- Absorbency: Spunlace nonwoven fabric has an absorbency range of 6-10 ml/g, while airlaid nonwoven fabric has an absorbency range of 8-20 ml/g. This means that airlaid nonwoven fabric is generally more absorbent than spunlace nonwoven fabric.
- Softness: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is known for its high softness, while airlaid nonwoven fabric is generally less soft due to its more random and uneven structure.
B. Performance Properties
Spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric also have different performance properties that affect their suitability for different applications. Some of the key differences are:
- Barrier properties: Spunlace nonwoven fabric has good barrier properties against liquids, while airlaid nonwoven fabric is more porous and may not provide as much barrier protection.
- Insulation properties: Airlaid nonwoven fabric has good insulation properties due to its fluffy and bulky texture, while spunlace nonwoven fabric may not provide as much insulation.
- Cleaning properties: Spunlace nonwoven fabric is known for its good cleaning properties due to its soft and smooth texture, while airlaid nonwoven fabric may not be as effective for cleaning due to its more random and uneven structure.
- Customizability: Both spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric can be customized for different applications, but spunlace nonwoven fabric may offer more flexibility in terms of fiber selection, basis weight, and finish.
C. Cost Comparison
The cost of spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric depends on several factors, such as the fiber type, basis weight, production volume, and quality requirements. However, in general, airlaid nonwoven fabric is more expensive than spunlace nonwoven fabric, due to its more complex and energy-intensive manufacturing process, higher raw material costs, and limited production capacity.
V. Case Studies
To illustrate the differences between spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric, here are two case studies of their applications:
- Wet wipes: A manufacturer of wet wipes wants to choose between spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric for their product. They require good absorbency, softness, and strength, as well as cost-effectiveness and customizability.
After testing both fabrics, they decide to use spunlace nonwoven fabric for the following reasons:
- Spunlace nonwoven fabric provides a softer and smoother texture that is more suitable for skin contact.
- Spunlace nonwoven fabric has good absorbency and cleaning properties, which meet their requirements.
- Spunlace nonwoven fabric has better tensile strength and tear resistance, which ensures the integrity of the wipes during use.
- Spunlace nonwoven fabric is more cost-effective and easier to customize than airlaid nonwoven fabric, which fits their budget and needs.
- Feminine hygiene products: A manufacturer of feminine hygiene products wants to choose between spunlace nonwoven fabric and airlaid nonwoven fabric for their product. They require good absorbency, softness, and sustainability, as well as regulatory compliance and market competitiveness.
After testing both fabrics, they decide to use airlaid nonwoven fabric for the following reasons:
- Airlaid nonwoven fabric provides a higher level of absorbency and fluid distribution, which is critical for feminine hygiene products.
- Airlaid nonwoven fabric has a more bulky and cushioning texture, which enhances the comfort and fit of the products.
- Airlaid nonwoven fabric can be made from renewable and biodegradable fibers, such as wood pulp, which aligns with their sustainability goals and values.
- Airlaid nonwoven fabric meets the regulatory requirements and market expectations for feminine hygiene products, which ensures their quality and safety.
VI. Future Trends
The nonwoven industry is constantly evolving and innovating, and there are several future trends that may impact the development and adoption of spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics, such as:
- Sustainability: The demand for sustainable and eco-friendly nonwoven fabrics is increasing, and both spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics can be made from renewable and biodegradable fibers. However, there may be more emphasis on reducing the energy and water consumption of the manufacturing process, as well as increasing the recyclability and biodegradability of the end products.
- Digitalization: The use of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics, may improve the efficiency, accuracy, and customization of nonwoven production. This may result in faster and more cost-effective production of spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics, as well as more precise and tailored products for different applications.
- New applications: The nonwoven industry may explore new applications and markets for spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics, such as in the fields of electronics, energy, and aerospace. These applications may require higher performance properties, such as conductivity, flame resistance, and durability, which may challenge the current capabilities of spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics.
VII. Conclusion
Spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics are two popular types of nonwoven fabrics that have different characteristics and applications. Spunlace nonwoven fabric is known for its softness, strength, and barrier properties, and is commonly used for wipes, medical products, and home textiles. Airlaid nonwoven fabric is known for its absorbency, bulkiness, and insulation properties, and is commonly used for absorbent products, food packaging, and home and personal care products. Both fabrics have advantages and disadvantages that depend on the specific needs and requirements of each application. By understanding the differences between spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics, customers can make informed decisions and achieve optimal results for their products.
If you are interested in learning more about spunlace and airlaid nonwoven fabrics, or if you need help choosing the right nonwoven fabric for your application, please contact us at Wanhua Nonwovens. We are a leading nonwoven manufacturer and supplier that provides high-quality, cost-effective, and customized solutions for a wide range of industries and applications. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve your goals and exceed your expectations. Thank you for reading this article, and we look forward to hearing from you soon.
Mandy Hong
Mob./Cell:0086-13599755808(WhatsApp/ Viber/Wechat/ Line)
Email:info@non-woven.com