Introduction
Nonwoven materials represent a cutting-edge class of fabrics created from fibers bonded together through an array of methods, such as chemical, mechanical, or thermal techniques. Unlike conventional woven or knitted fabrics, these materials do not necessitate intricate weaving processes. This distinctive production method lends nonwoven fabrics their unique properties, enabling widespread utility across diverse sectors.
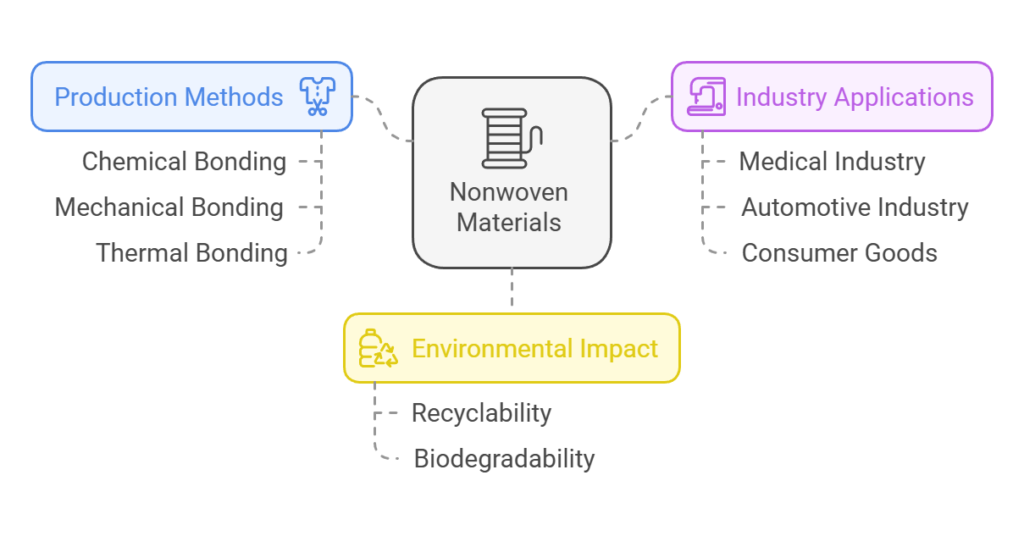
The versatility of nonwoven materials has led to their substantial adoption in industries such as medical, automotive, and consumer goods. In the medical field, for instance, nonwoven fabrics are integral to the manufacture of surgical masks, gowns, and wound dressings, ensuring sterility and providing critical protection against infections. In the automotive industry, these materials are employed in the production of various components, including insulation and filters, where their specific attributes such as durability and filtration efficiency are highly valued.
Consumer goods, too, have benefited immensely from nonwoven materials. Everyday products such as diapers, wipes, and feminine hygiene products owe their enhanced absorbency, softness, and cost-effectiveness to nonwoven technologies. The adaptability of these materials allows for customization to meet specific functional requirements and aesthetic preferences, further solidifying their significance.
Moreover, the environmental impact of nonwoven materials is worth noting. Many of these fabrics are designed to be recyclable or biodegradable, making them an eco-friendly option in an era increasingly focused on sustainability. This environmental consideration adds an additional layer of appeal to nonwoven materials, positioning them as a forward-thinking choice for the future.
Overall, the development and use of nonwoven materials demonstrate a significant advancement in material science, underscoring the importance of innovation and versatility in meeting the demands of modern industries and consumers alike. The following sections will delve deeper into the manufacturing processes, specific applications, and the advantages that make nonwoven materials indispensable in today’s world.
What is Nonwoven Material?
Nonwoven materials are unique types of fabrics produced by bonding or interlocking fibers through various methods. Unlike traditional woven fabrics, where fibers are interlaced, nonwoven fabrics are created using techniques such as chemical bonding, mechanical needling, or thermal bonding. These distinctive processes impart inherent properties to the material, such as enhanced durability and resistance to fraying, thereby extending its lifespan and usability across diverse applications.
One of the significant advantages of nonwoven materials is their versatility in fiber composition. The fibers can be sourced from natural origins, such as cotton, which provides softness and biodegradability. Alternatively, synthetic fibers like polyester can be employed, offering robustness, resistance to moisture, and cost-effectiveness. In many cases, a blend of both natural and synthetic fibers is used, combining the benefits of each to impart specific characteristics tailored to particular needs.
The process of creating nonwoven material begins with selecting the appropriate fibers, which are then arranged into a web. This web can be formed by several methods, including dry-laid, wet-laid, or spunlaid processes. Following web formation, the fibers are bonded together. Chemical bonding involves using adhesives to fuse the fibers, while mechanical needling uses barbed needles to entangle the fibers physically. Thermal bonding, on the other hand, employs heat to melt synthetic fibers, which then stick together upon cooling. Each bonding method has distinct advantages and is chosen based on the desired properties of the final fabric.
Due to their unique construction and the versatility in raw material choices, nonwoven materials find applications in numerous industries, ranging from medical supplies and hygiene products to automotive interiors and construction materials. Their ability to provide customized solutions while maintaining cost-efficiency makes nonwoven materials integral to many modern-day products.
Types of Nonwoven Materials
Nonwoven materials are classified based on their manufacturing processes, which impart distinct characteristics suitable for various applications. The most commonly recognized types include spunbond, meltblown, and spunlace nonwovens. Understanding these types and their specific attributes is essential in selecting the right material for a given application.
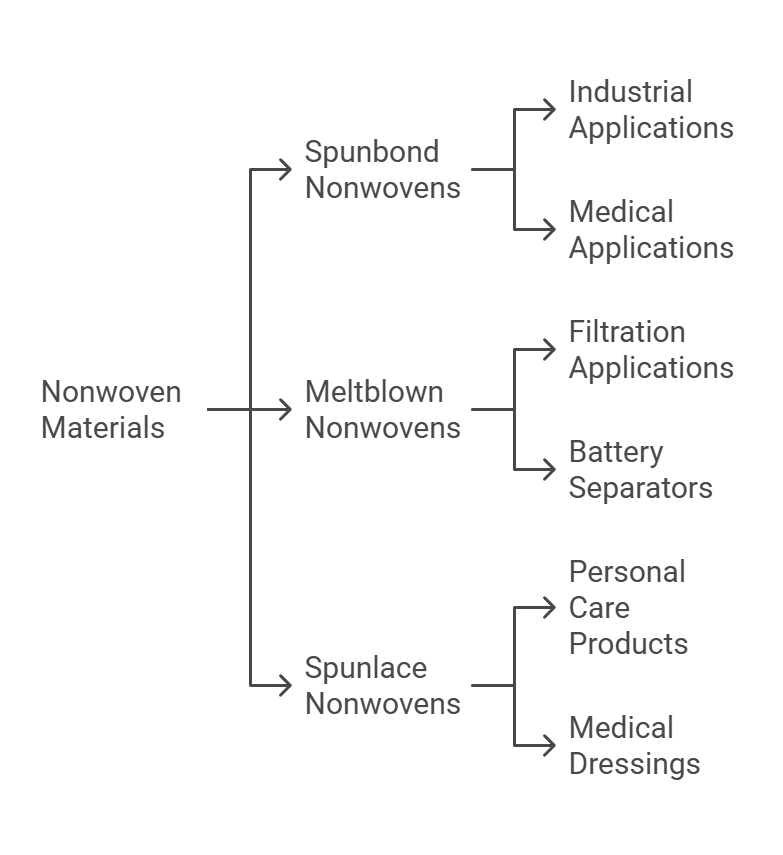
Spunbond nonwovens are produced through a process that involves extruding polymer filaments to form a web. This method results in a material that boasts high tensile strength and durability. Due to these properties, spunbond nonwoven materials are widely used in industrial applications such as geotextiles, roofing sheets, and agricultural covers. They are also prevalent in medical products like disposable gowns and bed sheets.
Meltblown nonwovens, on the other hand, are made by extruding molten polymer through tiny nozzles and blowing them with high-speed air streams. This process generates fine fibers that are randomly deposited to form a web with excellent filtration properties. Consequently, meltblown nonwoven materials are predominantly used in applications requiring fine filtration, such as surgical masks, respirators, and liquid filters. Their fine structure also makes them suitable for battery separators and oil absorbents.
Spunlace, or hydroentangled nonwovens, are created by entangling fibers using high-pressure water jets. This process yields a fabric with a soft hand-feel and good absorbency. Spunlace nonwoven materials are extensively used in personal care products such as wipes, cosmetic face masks, and hygiene products. Additionally, they find application in medical dressings and cleaning cloths due to their absorbent nature and gentle texture.
Each type of nonwoven material, with its unique set of properties, is designed to meet the specific needs of different industries. By leveraging the strengths of spunbond, meltblown, and spunlace nonwovens, manufacturers can optimize product performance and fulfill diverse application requirements efficiently.
Applications in the Medical Field
Nonwoven materials have become indispensable in the medical field due to their unique properties, such as disposability, hygiene, and effective barrier capabilities. These materials are extensively used in various medical applications. One primary use is in the production of surgical gowns. The nonwoven fabric offers a reliable barrier against infections, safeguarding both patients and healthcare professionals during surgical procedures.
Similarly, face masks made from nonwoven materials are crucial in preventing the spread of pathogens. The mask’s fabric is designed to filter out harmful particles, providing a vital layer of protection for individuals in clinical settings as well as the general public. Nonwoven materials’ breathability and lightweight nature make masks comfortable to wear, ensuring compliance and effectiveness.
Wound dressings also benefit from the properties of nonwoven materials. They offer excellent absorbency, which is essential for managing exudates and promoting wound healing. Additionally, the hypoallergenic nature of the material ensures it is gentle on sensitive skin, reducing the risk of irritation and infection.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of nonwoven materials was highlighted like never before. The demand for personal protective equipment (PPE) surged, leading to an increased need for masks, gowns, and other protective gear, all primarily manufactured from nonwoven fabrics. This surge underscored the critical role nonwoven materials play in public health and safety.
Use in the Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, nonwoven materials have become a pivotal component due to their versatility and performance benefits. Their application ranges from insulation to filtration and sound absorption, making them an invaluable asset to vehicle manufacturing. The lightweight and durable nature of nonwoven materials contribute significantly to the efficiency and efficacy of various automotive parts.
One of the primary uses of nonwoven materials in automobiles is for insulation. These materials possess excellent thermal properties, which make them ideal for maintaining temperature control within the vehicle. Whether managing heat from the engine compartment or maintaining cabin comfort, nonwoven materials provide effective thermal barriers.
Filtration is another critical function of nonwoven materials in vehicles. These materials are employed in engine air filters, cabin air filters, and oil filters, effectively removing contaminants and ensuring the longevity and performance of engine and HVAC systems. The fine structure of nonwoven materials enables them to capture particles and debris, which enhances vehicle efficiency and reduces wear and tear.
Sound absorption is equally essential in the automotive industry, and nonwoven materials excel in this area. They are used in headliners, carpets, and trunk liners to dampen noise and vibrations, contributing to a quieter and more comfortable ride. The ability of nonwoven materials to absorb sound waves helps in reducing road, wind, and engine noise, thereby enhancing the overall passenger experience.
Meeting stringent requirements for vehicle safety, comfort, and performance is crucial for automotive manufacturers. Nonwoven materials help achieve these benchmarks due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, resistance to chemicals and moisture, and customization capabilities. As a result, they are not only used in internal components but also in exterior parts such as protective underbody shields.
Overall, the innovative use of nonwoven materials in the automotive industry underscores their importance in modern vehicle engineering, contributing to advancements in safety, comfort, and performance.
Consumer and Household Products
Nonwoven materials have become indispensable in the realm of consumer and household products, largely due to their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and the convenience they offer. One prominent category where nonwoven materials excel is personal hygiene products. Diapers, both for infants and adults, rely heavily on the unique properties of nonwoven fabrics. These materials provide the necessary absorbency, softness, and breathability, ensuring comfort and effectiveness. Moreover, they enable these products to be both lightweight and disposable, enhancing convenience for users.
Another critical use of nonwoven materials in the household is wet wipes. Whether for baby care, personal hygiene, or general cleaning, wet wipes benefit from the strength and absorbency of nonwoven fabrics. They can hold up to rigorous cleaning tasks while offering a gentle touch, a combination that is hard to match with traditional woven fabrics. The single-use nature of these products also plays a key role in maintaining hygiene, preventing cross-contaminations that can occur with reusable items.
Cleaning cloths made from nonwoven materials are another innovation that has become a household staple. These cloths often feature enhanced durability and absorbency, making them ideal for a variety of cleaning tasks, from dusting furniture to scrubbing kitchen counters. They are designed to be disposed of after use, which aligns with modern demands for hygiene and convenience. A significant advantage of nonwoven cleaning cloths is their ability to be produced with different textures and impregnated with cleaning agents, offering tailored solutions for specific cleaning needs.
In essence, the integration of nonwoven materials in consumer and household products underscores their pivotal role in meeting hygiene standards and providing practical solutions for everyday tasks. Their adaptability and efficiency ensure that they remain a cornerstone in the creation of products that align with contemporary lifestyle demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nonwoven materials, celebrated for their versatility and range of applications, do come with environmental concerns that warrant careful attention. One of the main issues relates to their composition; many nonwoven fabrics are made from synthetic polymers like polypropylene and polyester, which do not readily decompose in the environment. This poses a significant challenge, especially given the increasing global emphasis on reducing plastic waste.
In response, the nonwoven industry is making concerted efforts to mitigate these environmental impacts. A major area of focus is the development and production of biodegradable nonwoven materials. These innovative products aim to balance functionality with environmental responsibility, breaking down more readily than conventional nonwovens and reducing long-term waste accumulation. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards using natural and renewable fibers such as cotton, bamboo, and viscose. These fibers not only lessen dependency on petroleum-based products but also provide a biodegradable alternative to traditional nonwovens.
Recycling initiatives are also gaining traction within the industry. Nonwoven production facilities are increasingly implementing closed-loop systems, where waste materials generated during manufacturing are captured and reused, significantly decreasing the amount of waste produced. The development of recyclable nonwoven materials is another avenue being pursued, allowing the products to re-enter the production cycle after their initial use, thereby conserving resources and reducing landfill deposits.
Another pivotal aspect of sustainability in nonwoven production involves the minimization of energy and water usage during the manufacturing process. Techniques such as airlaid and spunlace technology are being optimized to enhance efficiency and lower the environmental footprint. Additionally, the use of environmentally friendly adhesives and binders is being explored to ensure that nonwoven products comply with stringent ecological standards.
While challenges remain, the nonwoven industry is actively adapting to meet environmental concerns, striving towards sustainable practices that promise a reduced ecological impact without compromising on the material’s beneficial properties.
FAQs
Understanding nonwoven materials can often lead to several questions. Below are common inquiries regarding these versatile fabrics.
What are the benefits of nonwoven materials?
Nonwoven materials come with a plethora of benefits. One of the primary advantages is their cost-effectiveness; they are generally cheaper to produce than woven fabrics. They also allow for a high degree of customization in terms of weight, thickness, and texture, making them suitable for a variety of applications. Nonwovens are known for their durability, flexibility, and ability to be engineered with specific properties such as absorbency, repellency, elasticity, and sterility, which are critical for certain industries like medical and hygiene.
How are nonwoven materials different from woven fabrics?
The fundamental difference between nonwoven and woven fabrics lies in their manufacturing process. Woven fabrics are made by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles to each other, while nonwoven materials are made by bonding or interlocking fibers through mechanical, chemical, or thermal means. This gives nonwoven materials a unique texture and set of properties, such as enhanced strength and durability, that can be better suited for specific applications where traditional woven fabrics may fall short.
Are nonwoven materials biodegradable?
The biodegradability of nonwoven materials depends largely on the types of fibers and bonding agents used in their manufacture. For example, natural fibers like cotton or bamboo will decompose more readily than synthetic fibers such as polyester or polypropylene. However, advancements in eco-friendly nonwoven technology have made it possible to create biodegradable or even compostable nonwovens, which help mitigate the environmental impact typically associated with non-sustainable materials.
What are the most common uses of nonwoven materials?
Nonwoven materials are extremely versatile and are used in a wide range of industries. Common applications include medical textiles like gowns, masks, and surgical drapes due to their sterility and durability. In the hygiene sector, they are used in products like diapers and sanitary napkins for their absorbency and softness. Other prominent uses span from automotive interiors to filters, geotextiles in construction, and even consumer products like reusable shopping bags and cleaning wipes.




33 Responses
Hi Neat post Theres an issue together with your web site in internet explorer may test this IE still is the marketplace chief and a good component of people will pass over your fantastic writing due to this problem
Real Estate This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
Thank you for your kind words! I’m thrilled to hear you enjoyed the post. Your appreciation means a lot. Stay tuned for more content!
Thank you for the auspicious writeup It in fact was a amusement account it Look advanced to far added agreeable from you However how can we communicate
Thank you for your kind words! I’m glad you enjoyed the write-up. Feel free to reach out through the contact form on our website or via direct message on our social media channels. Looking forward to hearing from you!
Baddiehubs I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will
Thanks! Glad you like it.
I have learn several good stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how much attempt you place to make any such fantastic informative web site.
Thank you for your kind words! We’ll keep working hard to provide valuable content. 😊
Hmm it seems like your website ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any tips for beginner blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
Thanks for your compliment! For beginner blog writers, I suggest finding a unique niche, being consistent in posting, and engaging with your readers. Good luck with your blogging journey!
F*ckin’ amazing issues here. I am very satisfied to peer your article. Thanks a lot and i’m looking ahead to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Thank you for your comment! Glad you liked the article. You can contact me at [your email address]. Looking forward to hearing from you.
I got what you mean , appreciate it for posting.Woh I am glad to find this website through google.
Glad you found value in it. Thanks for your kind words!
Mat6tube I enjoy your web page, but it’s worth checking the spelling in a number of posts. Some of them contain errors that I find a bit irritating, yet I’ll surely visit again.
Thank you so much for your kind words about our website and for taking the time to provide feedback. We truly appreciate your honesty. We’ll immediately have our team review the posts and correct any spelling errors. We’re glad to hear that despite this, you’ll be back, and we’re committed to providing you with a better reading experience in the future.
I went over this web site and I conceive you have a lot of superb info , saved to bookmarks (:.
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that you appreciate our content. We strive to provide valuable and engaging information rather than just focusing on gossip.
Regarding newsletters, we do have one. You can usually find the subscription option at the bottom of our website pages. If you still can’t locate it, please let us know, and we’ll guide you through the process.
Valuable information. Fortunate me I discovered your website unintentionally, and I am stunned why this coincidence didn’t took place in advance! I bookmarked it.
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled that you stumbled upon our site and found the information valuable. We hope you’ll continue to find useful content here. If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to let us know.
Some really interesting information, well written and broadly speaking user genial.
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled that you found the information interesting and the article well – written. Your positive feedback means a lot to us, and we hope you’ll continue to explore more content on our site.
magnificent submit, very informative. I wonder why the opposite specialists of this sector do not notice this. You should continue your writing. I am sure, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Thank you so much for your kind words! Your encouragement means the world to us. We’ll definitely keep up the good work and strive to bring more valuable content. We’re glad you found the article informative, and we hope you’ll stay tuned for future posts!
I got what you intend,saved to fav, very decent internet site.
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled that you found the content valuable and decided to save us to your favorites. If you have any suggestions or topics you’d like to see covered in the future, feel free to let us know. We hope you continue to enjoy browsing our non – woven website!
As I web site possessor I believe the content material here is rattling magnificent , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
Thank you so much for your kind words! Your support means the world to us. We’ll definitely keep up the good work and strive to bring you more great content. Have a wonderful day!
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Glad you think so! Thanks for your kind words.
Greetings from Idaho! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break. I love the knowledge you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m surprised at how quick your blog loaded on my cell phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, amazing site!
Thank you for your kind words! Glad the site loads quickly for you. Enjoy exploring when you get home! 😊