Nonwoven Fabric: An Innovation in the Field of Textile Materials
With the continuous advancement in material science, nonwoven fabric, known for its unique production process and extensive application fields, has become an indispensable material in industries, healthcare, agriculture, and everyday life. This article aims to delve into the definition, production process, main characteristics, application fields of nonwoven fabric, and the environmental challenges it faces from a scientific perspective.
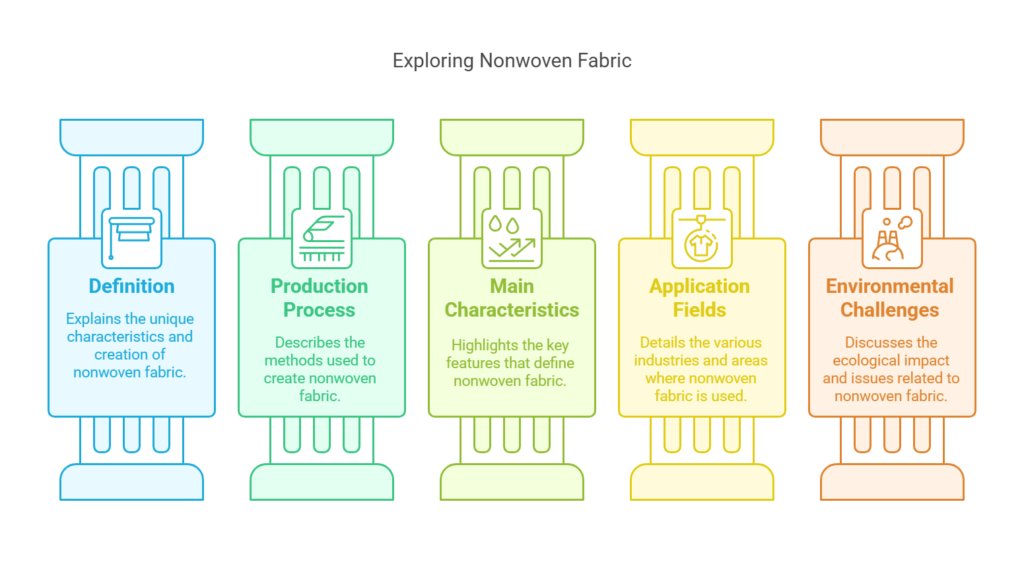
1. Scientific Definition of Nonwoven Fabric: Nonwoven fabric, also known as nonwoven cloth, is a novel type of fabric that is created by directly bonding short fibers or filaments through mechanical, thermal, or chemical methods. Unlike traditional fabrics woven from threads, the production process of nonwoven fabric does not rely on looms, hence the name “nonwoven.”
2. The Science of Nonwoven Fabric Production: The production process of nonwoven fabric involves a series of precise scientific steps:
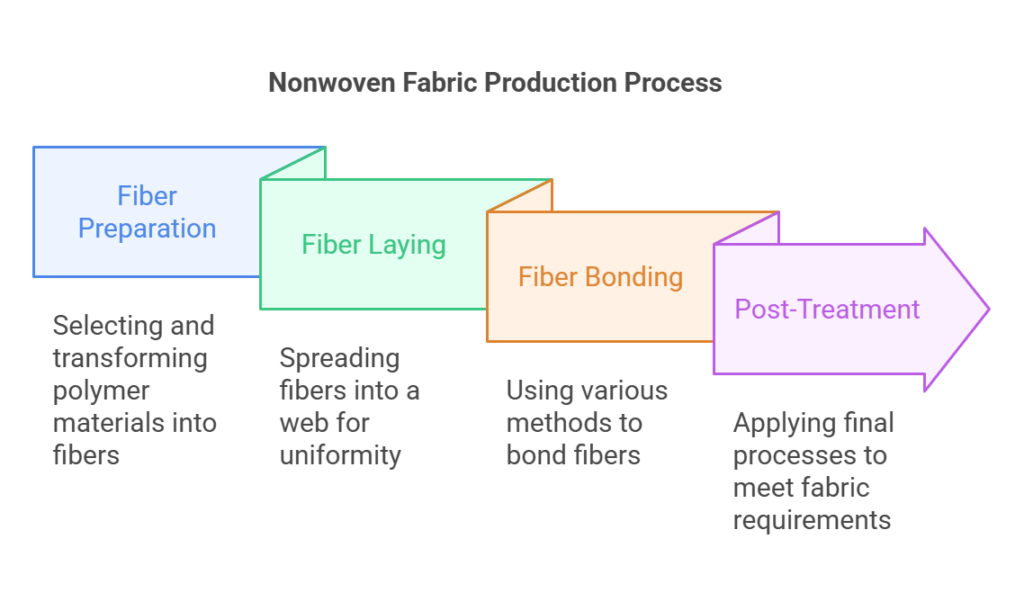
- Fiber Preparation: Select appropriate polymer materials such as polypropylene or polyester and transform them into short fibers or filaments through melting or cutting processes, laying the foundation for subsequent nonwoven fabric production.
- Fiber Laying: Utilize precise engineering techniques to evenly spread short fibers or filaments into a fiber web, a step crucial for the uniformity and strength of the fabric.
- Fiber Bonding: Use the following scientific technologies to bond fibers together to form a stable fabric structure:
- Needle Punched Method: Mechanically entangle fibers using barbed needles, suitable for producing thicker nonwoven fabrics.
- Spunlace Method: Physically intertwine fibers in a web through high-speed water jets, suitable for producing delicate and uniform nonwoven fabrics.
- Thermal Calendering: Partially melt and bond fibers through high-temperature calendering, commonly used for producing disposable sanitary products.
- Chemical Bonding: Use chemical adhesives to bond fibers together through chemical reactions, suitable for nonwoven fabrics that require a soft feel.
- Post-Treatment: Depending on the final application, nonwoven fabric may need to undergo post-treatment processes such as coating, printing, cutting, and folding to meet specific application requirements.
3. Scientific Properties of Nonwoven Fabric:
The scientific properties of nonwoven fabric are the basis for its wide range of applications:
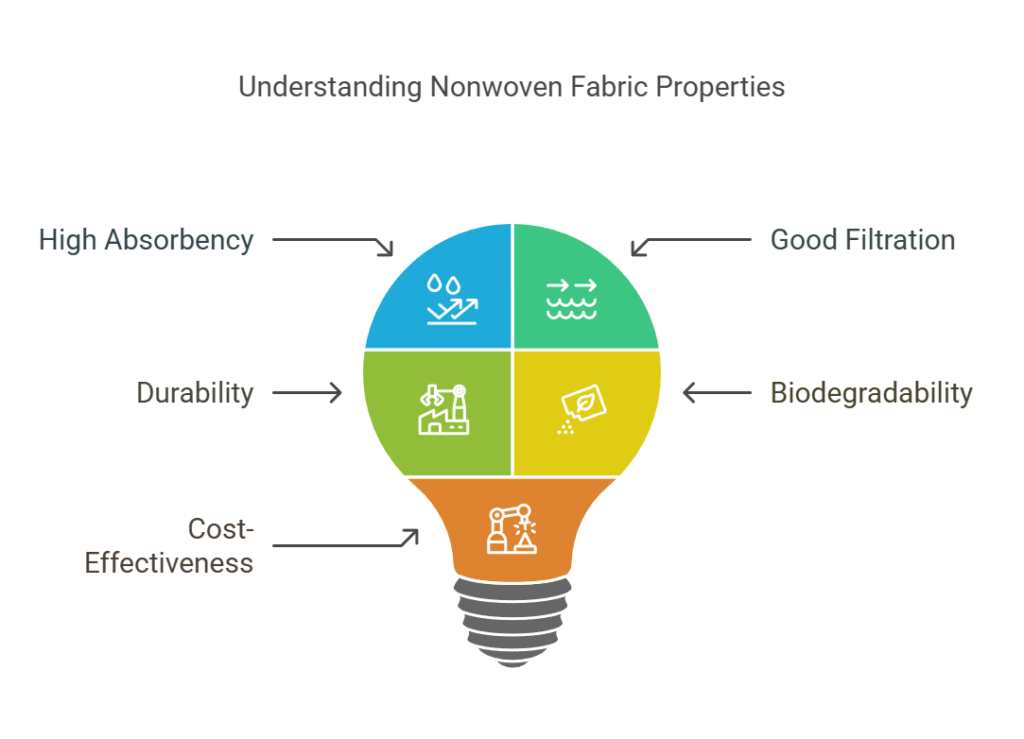
- High Absorbency: Suitable for cleaning products and personal care items such as wet wipes and sanitary pads.
- Good Filtration: The porous structure of nonwoven fabric makes it an ideal choice for air and liquid filtration systems.
- Durability: Exhibits high tensile strength and durability, suitable for manufacturing durable industrial products.
- Biodegradability: Although most nonwoven fabric materials like polypropylene are not biodegradable, some nonwoven fabrics made from bio-based materials such as polylactic acid (PLA) are biodegradable and environmentally friendly.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The production process is relatively simple, and the cost is low, making it suitable for mass production.
Table. Properties of Nonwoven :
| Property | Description | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| High Absorbency | Rapid liquid absorption | Wet wipes, sanitary pads |
| Good Filtration | Porous structure for filtering | Masks, filter bags |
| Durability | High tensile strength | Industrial products |
| Biodegradability | Environmentally friendly | Some bio-based materials |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Simple production | Mass production suitability |
4. Scientific Applications of Nonwoven Fabric:
The scientific applications of nonwoven fabric are extensive and cover:
- Medical Industry: Nonwoven fabric is popular in the medical field for applications such as surgical gowns, masks, hats, bed sheets, and medical gauze, due to its sterile and disposable characteristics.
- Personal Care: Sanitary pads, diapers, cosmetic cotton, wet wipes, etc., utilize the soft, absorbent, and hygienic properties of nonwoven fabric.
- Agriculture: Crop protection cloth, insulation materials, weed control cloth, etc., where nonwoven fabric helps improve the growing environment and protect crops.
- Industrial Uses: Filtration materials, insulating materials, reinforcement materials, etc., where the durability and functionality of nonwoven fabric are widely applied.
- Household Products: Disposable tablecloths, cleaning cloths, shopping bags, etc., where the convenience and cost-effectiveness of nonwoven fabric make it an ideal choice for household products.
Table : Application of Nonwoven
| Application Field | Specific Uses |
|---|---|
| Medical Industry | Surgical gowns, masks, hats, bed sheets, medical gauze |
| Personal Care | Sanitary pads, diapers, cosmetic cotton, wet wipes |
| Agriculture | Crop protection cloth, insulation materials, weed control cloth |
| Industrial Uses | Filtration materials, insulating materials, reinforcement materials |
| Household Products | Disposable tablecloths, cleaning cloths, shopping bags |
5. Environmental Challenges of Nonwoven Fabric: The environmental challenge of nonwoven fabric mainly lies in its non-biodegradable nature, which can lead to environmental pollution if not properly disposed of. To address this challenge, the scientific and industrial communities are:
- Developing New Materials: Researching and developing biodegradable nonwoven fabric materials such as polylactic acid (PLA) to reduce environmental impact.
- Improving Recycling Rates: Encouraging and promoting the recycling and reuse of nonwoven fabrics to reduce the environmental issues caused by landfilling and incineration.
- Environmental Awareness Education: Raising public awareness of the environmental issues of nonwoven fabrics and advocating for their reasonable use and disposal, such as replacing disposable nonwoven bags with reusable shopping bags.
6. Further Exploration: The future development direction of nonwoven fabric may include the following scientific fields:
- Technological Innovation: Developing new production technologies to enhance the performance of nonwoven fabric, such as increasing its strength, durability, and comfort.
- Multifunctionality: Combining different materials and technologies to create nonwoven fabrics with various functions, such as antibacterial, UV-resistant, and flame-retardant properties.
- Intelligentization: Utilizing intelligent technologies, such as sensors and micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS), to develop smart nonwoven fabric products, such as medical clothing that can monitor health conditions.
- Personalized Customization: As consumer demand for personalized products increases, the nonwoven fabric industry can offer more customized services to meet the needs of different consumers.
The development prospects of nonwoven fabric are broad, but it also faces challenges in environmental protection and sustainable development. Through continuous technological innovation and improved environmental awareness, the nonwoven fabric industry is expected to achieve more green, efficient, and intelligent development.
Conclusion:
Nonwoven fabric, as a versatile material, plays an important role in modern society. With the advancement of technology and increased environmental awareness, the production and application of nonwoven fabric will pay more attention to sustainability to reduce its environmental impact.
We encourage consumers to choose environmentally friendly nonwoven fabric products, participate in recycling programs, and raise environmental awareness to reduce the impact of nonwoven fabric on the environment. At the same time, we also call on related enterprises and research institutions to continue exploring more environmentally friendly production methods and materials to jointly promote the green development of the nonwoven fabric industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
- Q: What is the primary difference between nonwoven and traditional woven fabrics? A: Nonwoven fabrics are made from short fibers or filaments that are bonded together directly, without the need for weaving or knitting, which is a characteristic process of traditional fabrics.
- Q: Are all nonwoven fabrics disposable? A: Not all nonwoven fabrics are disposable. While many are designed for single-use applications in medical and personal care products, there are also durable nonwoven fabrics used in industrial and agricultural applications that are not intended for disposal after a single use.
- Q: How can nonwoven fabrics be made more environmentally friendly? A: Nonwoven fabrics can be made more environmentally friendly by using biodegradable materials like polylactic acid (PLA), improving recycling processes, and promoting the use of reusable nonwoven products.
- Q: What are some common misconceptions about nonwoven fabrics? A: A common misconception is that all nonwoven fabrics are the same. In reality, they can vary significantly in terms of their composition, properties, and intended applications.
- Q: Can nonwoven fabrics be recycled? A: Yes, recycling of nonwoven fabrics is possible and is an active area of development. However, the recycling process can be challenging due to the different materials and bonding methods used in their production.
- Q: Are there any health benefits to using nonwoven fabrics in medical applications? A: Nonwoven fabrics are used in medical applications due to their sterile nature and ability to be disposed of after use, which helps prevent cross-contamination and reduce the spread of infections.
- Q: What role do intelligent technologies play in the future of nonwoven fabrics? A: Intelligent technologies, such as sensors and MEMS, can be integrated into nonwoven fabrics to create smart textiles that can monitor health conditions or respond to environmental changes, enhancing their functionality.
- Q: How does the nonwoven fabric industry contribute to sustainable development? A: The industry contributes to sustainable development by focusing on eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient production processes, and the development of products that can be recycled or have a lower environmental impact.
- Q: What are some potential applications of nonwoven fabrics in the future? A: Future applications may include advanced personal protective equipment, smart home textiles with integrated electronics, and innovative agricultural products that improve crop yield and sustainability.
- Q: How can consumers support the use of eco-friendly nonwoven fabrics? A: Consumers can support eco-friendly nonwoven fabrics by choosing products made from recycled or biodegradable materials, properly recycling used nonwoven products, and advocating for more sustainable manufacturing practices.
By addressing these FAQs, we can provide readers with a deeper understanding of nonwoven fabrics and their role in various industries, as well as the steps being taken to ensure their environmental sustainability.